Wild Weasels

 The 931.OGRAP experienced a significant change in 1986. The regiment was composed of two squadrons, the first flying different MiG-25RB variants and the second on Yak-28R.
However, in June, the Yak-28R were sent to Welzow where they joined those of the local 11.ORAP in preparation for their withdrawal from Germany. The last Yak-28R still based in the
former GDR left Welzow on July 2, 1986. Also in June, the Yak-28PP of the third squadron from the 11.ORAP departed Welzow for Werneuchen where they reconstituted the second
squadron of the 931.OGRAP. Thus, when those changes were completed, this unit became a composite reconnaissance and electronic warfare regiment (for a description of the Yak-28PP,
refer to the first page about the 11.ORAP).
In addition, a third electronic warfare squadron was established within the 931.OGRAP when twelve MiG-25BM "Foxbat-F" (some of those aircraft were among the last one built)
and three MiG-25RU "Foxbat-C" arrived soon thereafter. The last aircraft landed at Werneuchen in late 1986.
The 931.OGRAP experienced a significant change in 1986. The regiment was composed of two squadrons, the first flying different MiG-25RB variants and the second on Yak-28R.
However, in June, the Yak-28R were sent to Welzow where they joined those of the local 11.ORAP in preparation for their withdrawal from Germany. The last Yak-28R still based in the
former GDR left Welzow on July 2, 1986. Also in June, the Yak-28PP of the third squadron from the 11.ORAP departed Welzow for Werneuchen where they reconstituted the second
squadron of the 931.OGRAP. Thus, when those changes were completed, this unit became a composite reconnaissance and electronic warfare regiment (for a description of the Yak-28PP,
refer to the first page about the 11.ORAP).
In addition, a third electronic warfare squadron was established within the 931.OGRAP when twelve MiG-25BM "Foxbat-F" (some of those aircraft were among the last one built)
and three MiG-25RU "Foxbat-C" arrived soon thereafter. The last aircraft landed at Werneuchen in late 1986.

 The MiG-25BM (Bombardirovshchik Modifikatsirovanyy - Bomber Modified) "Foxbat-F" were the only aircraft within the 16.VA inventory specifically designed
to detect and destroy radar sites, SAM batteries and also underground command posts. This aircraft type was assigned to reconnaissance units equipped with MiG-25s, for operational
conversion and logistical reasons. Also, the reconnaissance eskadril'i provided relevant information about the MiG-25BM targets.
Another MiG-25BM squadron was based at Brzeg in Poland, where it operated within the 164.OGRAP, while a third and last squadron flew
within the 10.ORAP at Shchuchin in Belarus.
Note, however, that SEAD missions (Suppression of Enemy Air Defences) were not new nor did they rest upon the MiG-25BM shoulders alone.
First, Su-17M2 and M3 (and some upgraded Su-17M) and Su-24 could fire Kh-28 (AS-9 "Kyle") anti-radiation missiles (ARM). The Su-17M2/M3 had to carry a
Metel'-A (Blizzard) designation pod and the Su-24 a Filin-N (Eagle Owl) pod that was later mounted internally. Then, MiG-27D/M/K, Su-17M3 and M4 as well as Su-24M
could fire Kh-25MP and Kh-27PS (AS-12 "Kegler" - same designations for these two missiles) ARM. The MiG-27D/M/K and the Su-17M3/M4 had to use a
V'yuga (Snowstorm) designation pod and the Su-24M a Fantasmagoriya (Phantasmagoria) pod in order to be able to fire these weapons.
The MiG-25BM (Bombardirovshchik Modifikatsirovanyy - Bomber Modified) "Foxbat-F" were the only aircraft within the 16.VA inventory specifically designed
to detect and destroy radar sites, SAM batteries and also underground command posts. This aircraft type was assigned to reconnaissance units equipped with MiG-25s, for operational
conversion and logistical reasons. Also, the reconnaissance eskadril'i provided relevant information about the MiG-25BM targets.
Another MiG-25BM squadron was based at Brzeg in Poland, where it operated within the 164.OGRAP, while a third and last squadron flew
within the 10.ORAP at Shchuchin in Belarus.
Note, however, that SEAD missions (Suppression of Enemy Air Defences) were not new nor did they rest upon the MiG-25BM shoulders alone.
First, Su-17M2 and M3 (and some upgraded Su-17M) and Su-24 could fire Kh-28 (AS-9 "Kyle") anti-radiation missiles (ARM). The Su-17M2/M3 had to carry a
Metel'-A (Blizzard) designation pod and the Su-24 a Filin-N (Eagle Owl) pod that was later mounted internally. Then, MiG-27D/M/K, Su-17M3 and M4 as well as Su-24M
could fire Kh-25MP and Kh-27PS (AS-12 "Kegler" - same designations for these two missiles) ARM. The MiG-27D/M/K and the Su-17M3/M4 had to use a
V'yuga (Snowstorm) designation pod and the Su-24M a Fantasmagoriya (Phantasmagoria) pod in order to be able to fire these weapons.
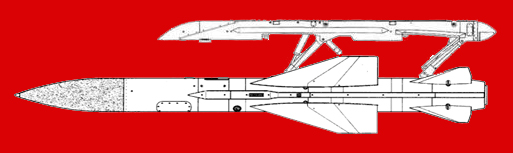
 MiG-25RBM, alias Article 66 or 02M (1) - designated MiG-25BM at squadon level - was developed in 1976.
Based on the "Foxbat" reconnaissance and bombardment variant (a MiG-25RBV "Foxbat-B" airframe was used as testbed), it was developed as a platform for the
Kh-58 (AS-11 "Kilter") anti-radiation misile (2). Only 40 aircraft were manufactured at Gor'kiy between
1982 and 1986. The MiG-25BM carried an integrated radar detection and electronic countermeasures suite called Yaguar (Jaguar) that required
a 20-centimeter nose extension. The suite included the modified PRGS-58M (Passivnaya Radiolokatsionnaya Golovka Samonavedeniya - Passive Radar Seeker)
missile seeker head, a Sych-M (Owl) control and target designation system, a SPS-151 OZh Siren-1D-OZh (Lilac) active ECM complex and
a SPS-135 Lyutik (Buttercup) passive noise generator module that were used to jam ground defence radars and, finally, a SPO-15LM Bereza-LM
(Birch) RHWR that warned the pilot when his aircraft was locked by a ground-based or airborne radar.
The "Jaguar" complex worked in conjunction with the upgraded Peleng-2M navigation complex that was adapted to the programming parameters of the anti-radar missiles.
In addition, the aircraft were equipped with a Tangazh ELINT suite enabling them to also fulfill
electronic reconnaissance tasks along the German inner border. In an attempt to hide the true nature of the MiG-25BM, their nose
were covered with dark grey paint in order to give them the appearance of fighter-interceptor variants, an impression that was reinforced by their four wing pylons.
MiG-25RBM, alias Article 66 or 02M (1) - designated MiG-25BM at squadon level - was developed in 1976.
Based on the "Foxbat" reconnaissance and bombardment variant (a MiG-25RBV "Foxbat-B" airframe was used as testbed), it was developed as a platform for the
Kh-58 (AS-11 "Kilter") anti-radiation misile (2). Only 40 aircraft were manufactured at Gor'kiy between
1982 and 1986. The MiG-25BM carried an integrated radar detection and electronic countermeasures suite called Yaguar (Jaguar) that required
a 20-centimeter nose extension. The suite included the modified PRGS-58M (Passivnaya Radiolokatsionnaya Golovka Samonavedeniya - Passive Radar Seeker)
missile seeker head, a Sych-M (Owl) control and target designation system, a SPS-151 OZh Siren-1D-OZh (Lilac) active ECM complex and
a SPS-135 Lyutik (Buttercup) passive noise generator module that were used to jam ground defence radars and, finally, a SPO-15LM Bereza-LM
(Birch) RHWR that warned the pilot when his aircraft was locked by a ground-based or airborne radar.
The "Jaguar" complex worked in conjunction with the upgraded Peleng-2M navigation complex that was adapted to the programming parameters of the anti-radar missiles.
In addition, the aircraft were equipped with a Tangazh ELINT suite enabling them to also fulfill
electronic reconnaissance tasks along the German inner border. In an attempt to hide the true nature of the MiG-25BM, their nose
were covered with dark grey paint in order to give them the appearance of fighter-interceptor variants, an impression that was reinforced by their four wing pylons.
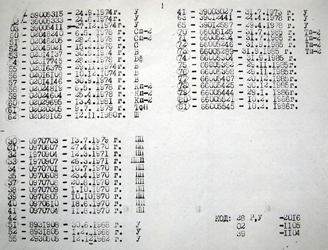
| ORBAT 1945 - 1993 |

 The MiG-25BM could carry up to four anti-radar missiles under its wings (only two missiles were planned during the design phase)
or a combination of missiles and bombs (up to eight FAB-500M-62AT bombs).
The "Foxbat-F" carried the Kh-58U variant of the "Kilter." It was built primarily of titanium and was designed to resist kinetic heating of 400 to 500°C.
The maximum Mach number with missiles was restricted to 2.38.
During their operational conversion, the pilots followed the Reconnaissance Aviation Combat Training Course
(Kurs Boyevoy Podgotovki Razvedyvatel'noy Aviatsii) to which the specificities of the MiG-25BM employment were added.
Kh-58 "without suffix" training missiles were proposed for the initial training, because of a shortage of Kh-58U. However, the Kh-58 also employed by other aircraft types such as
the Su-24 were limited to a speed not exceeding Mach 1.5 and therefore they could not be used for training.
The MiG-25BM would have penetrated enemy air defences essentially without entering their lethal zone. Besides, if it had been necessary to attack
NATO, targets would have been close to the front line. Thus, the approach to enemy territory would have been flown over friendly lines.
Also, takeoffs and landings were protected by fighter aircraft. Following a reconnaissance mission over the potential targets,
relevant data were entered into the different systems of the MiG-25BM such as the Peleng navigation complex.
The transit flight to the target area was achieved at high altitude to a range of 200 to 60 km from the target (200 km was considered
the maximum acceptable operational range, although successful firing were achieved at a range of 300 km from the target during tests with the Kh-58U variant.
However, there was the risk that the missiles' nickel-cadmium batteries would run down before reaching the target when firing from such a long range).
The target could be locked on from ranges up to 400 km.
The MiG-25BM could carry up to four anti-radar missiles under its wings (only two missiles were planned during the design phase)
or a combination of missiles and bombs (up to eight FAB-500M-62AT bombs).
The "Foxbat-F" carried the Kh-58U variant of the "Kilter." It was built primarily of titanium and was designed to resist kinetic heating of 400 to 500°C.
The maximum Mach number with missiles was restricted to 2.38.
During their operational conversion, the pilots followed the Reconnaissance Aviation Combat Training Course
(Kurs Boyevoy Podgotovki Razvedyvatel'noy Aviatsii) to which the specificities of the MiG-25BM employment were added.
Kh-58 "without suffix" training missiles were proposed for the initial training, because of a shortage of Kh-58U. However, the Kh-58 also employed by other aircraft types such as
the Su-24 were limited to a speed not exceeding Mach 1.5 and therefore they could not be used for training.
The MiG-25BM would have penetrated enemy air defences essentially without entering their lethal zone. Besides, if it had been necessary to attack
NATO, targets would have been close to the front line. Thus, the approach to enemy territory would have been flown over friendly lines.
Also, takeoffs and landings were protected by fighter aircraft. Following a reconnaissance mission over the potential targets,
relevant data were entered into the different systems of the MiG-25BM such as the Peleng navigation complex.
The transit flight to the target area was achieved at high altitude to a range of 200 to 60 km from the target (200 km was considered
the maximum acceptable operational range, although successful firing were achieved at a range of 300 km from the target during tests with the Kh-58U variant.
However, there was the risk that the missiles' nickel-cadmium batteries would run down before reaching the target when firing from such a long range).
The target could be locked on from ranges up to 400 km.
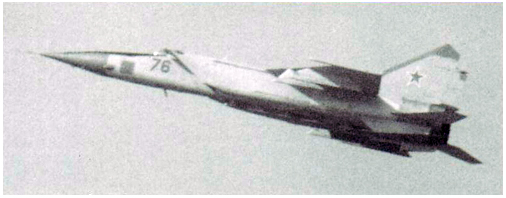 Décollage de Werneuchen du MiG-25BM n°76. © MLM.
Décollage de Werneuchen du MiG-25BM n°76. © MLM.
MiG-25BM n°76 taking off from Werneuchen. © MLM.
The missile seeker existed in four different versions, adapted to different radar frequency bands; moreover, they were not vulnerable to electronic countermeasures.
Each missile could be programmed separately so it was possible to carry missiles with different seekers simultaneously. The Sych-M system detected active radars
and selected their signals for input into the missile control system.
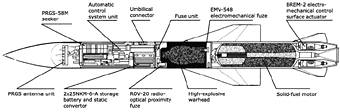
The missiles were attached to AKU-58 (Aviatsionnaya Katapul'tnaya Ustanovka
or literally aerial ejection unit) launch rails under the wing pylons. When fired, the Kh-58U missiles initially were separated from the aircraft by two extendable arms integrated into the AKU-58
and powered by compressed air. Thus, damage to the carrier aircraft was avoided when the missile engine was ignited and, above all, the risk of a reactor stall through gaz ingestion was eliminated.
The missile was launched at about Mach 2.35 maximum from an altitude between 17,000 and 21,000 meters.
The rocket engine provided 6 tons of thrust lasting 3.6 seconds, while the missile accelerated either upwards or in a downwards dive
depending on the range to the target. The thrust was then autonomously reduced simply by burning solid propellant
of a different caliber in a smaller combustion chamber, providing a sustained thrust of 1 ton for 15 seconds.
 The Yaguar had several operating modes. Thus, when the target coordinates were known, the PRGS-58M seeker aimed at the programmed coordinates; on the other hand, it locked onto the
selected radar when the latter was active. Should the radar emissions be interrupted after locking onto the target, the Kh-58U, a "Fire and Forget" weapon, nevertheless hit
its target because it could store in memory the last recorded target coordinates for 15 seconds. The "Kilter" was autonomous after firing,
making it possible for the pilot to maneuver or turn around. The final dive to the target occured at an angle of 45°.
The 149 kg missile warhead, including 58.5 kg of explosives (3), exploded up to five meters above the target or at impact.
The Yaguar had several operating modes. Thus, when the target coordinates were known, the PRGS-58M seeker aimed at the programmed coordinates; on the other hand, it locked onto the
selected radar when the latter was active. Should the radar emissions be interrupted after locking onto the target, the Kh-58U, a "Fire and Forget" weapon, nevertheless hit
its target because it could store in memory the last recorded target coordinates for 15 seconds. The "Kilter" was autonomous after firing,
making it possible for the pilot to maneuver or turn around. The final dive to the target occured at an angle of 45°.
The 149 kg missile warhead, including 58.5 kg of explosives (3), exploded up to five meters above the target or at impact.

 MiG-25BM squadrons regularly went to Akhtubinsk to conduct live fire exercises. Missiles always hit their target, even when the Blesna (Bait) simulators
replicating Hawk, Improved Hawk or Nike Hercules battery radar signals were turned off - but, of course, none of this took place on a real theater of operations.
Some MiG-25BM from Werneuchen were observed with small red stars painted on the upper part of their left engine air intakes, the latter
symbolizing successful missile firings. Also, an annual bombing campaign took place on the Luninets Bombing Range in Belarus.
The 931.OGRAP and its aircraft would soon bear the brunt of the unilateral disarmament policy initiated by Moscow and upheavals
in Europe in the late eighties.
Thus, dismantling of the 931.OGRAP squadron by squadron began with the Yak-28PP of the 2.AE that departed Werneuchen in July 1989 to join the 118.OAPREB
(Otdel'nyy Aviatsionnyy Polk Radioelektronnoy Bor'bi - Separate Electronic Warfare Aviation Regiment) at Chortkov airfield in Ukraine.
MiG-25BM squadrons regularly went to Akhtubinsk to conduct live fire exercises. Missiles always hit their target, even when the Blesna (Bait) simulators
replicating Hawk, Improved Hawk or Nike Hercules battery radar signals were turned off - but, of course, none of this took place on a real theater of operations.
Some MiG-25BM from Werneuchen were observed with small red stars painted on the upper part of their left engine air intakes, the latter
symbolizing successful missile firings. Also, an annual bombing campaign took place on the Luninets Bombing Range in Belarus.
The 931.OGRAP and its aircraft would soon bear the brunt of the unilateral disarmament policy initiated by Moscow and upheavals
in Europe in the late eighties.
Thus, dismantling of the 931.OGRAP squadron by squadron began with the Yak-28PP of the 2.AE that departed Werneuchen in July 1989 to join the 118.OAPREB
(Otdel'nyy Aviatsionnyy Polk Radioelektronnoy Bor'bi - Separate Electronic Warfare Aviation Regiment) at Chortkov airfield in Ukraine.

 In July 1990, the MiG-25BM were repatriated to Shchuchin (Belarussia) where they were assigned to the third squadron of the 151.OAPREB.
This regiment had vacated its former airbase located at Brzeg in Poland one year earlier, in August 1989. The first squadron was equipped with
the former MiG-25BM of the 164.OGRAP - also from Brzeg - whereas the second squadron flew with Yak-28PP.
Thus, all the MiG-25BM combat units (a handful of aircraft went through
Akhtubinsk, Lipetsk and Zhukovskiy) were consolidated in Shchuchin, where the 10.ORAP also was based, with the three squadrons equipped with MiG-25RB,
Su-24MR and MiG-25BM, respectively. All MiG-25BM were eventually sent to the Baranovichi Maintenance Center where they were destroyed between 1992 and 1995 in the framework of agreements
on the reduction of conventional forces in Europe (CFE Treaty) (4).
In July 1990, the MiG-25BM were repatriated to Shchuchin (Belarussia) where they were assigned to the third squadron of the 151.OAPREB.
This regiment had vacated its former airbase located at Brzeg in Poland one year earlier, in August 1989. The first squadron was equipped with
the former MiG-25BM of the 164.OGRAP - also from Brzeg - whereas the second squadron flew with Yak-28PP.
Thus, all the MiG-25BM combat units (a handful of aircraft went through
Akhtubinsk, Lipetsk and Zhukovskiy) were consolidated in Shchuchin, where the 10.ORAP also was based, with the three squadrons equipped with MiG-25RB,
Su-24MR and MiG-25BM, respectively. All MiG-25BM were eventually sent to the Baranovichi Maintenance Center where they were destroyed between 1992 and 1995 in the framework of agreements
on the reduction of conventional forces in Europe (CFE Treaty) (4).
An aircraft (n°44) was at Zaporozh'ye to undergo modifications. It survived there to this day (2013).
Another known survivor is former n°78 of the 931.OGRAP preserved at the Borovaya Museum in Belarus > LINK.
A third aircraft (n°43) is preserved in the museum at an airbase located in the North Caucasus > LINK.
notes
(1)
The existence of two different article numbers for a single aircraft type can be explained by the culture of secrecy and the use of different numbers by the manufacturer
and the VVS. The MiG-25R also had two different article numbers: 02 and 55.
(2)
The Kh-58 was declared fit for service in the early eighties. Its maximum range was 120 km. The Kh-58U was the next variant and it became operational
with the MiG-25BM in the mid-eighties. This version, equipped with a modified seeker and having its maximum range increased to 250 km,
was developed to be carried by other aircraft types such as the Su-17M3 and M4 that had to use a
V'yuga-14 external pod in order to designate targets. The Su-24 and Su-24M also used this missile in conjunction with a Fantasmagoriya designation pod.
The latter was available in different variants depending on the radar frequency bands to be covered. The speed of the Su-17 and Su-24 armed with two Kh-58 missiles was limited to a maximum of Mach 1.5.
The missile firing envelope was very different with these other aircraft compared to the MiG-25BM. Missiles were employed from the latter from a minimum altitude of 17,000 meters to increase
their range and the target acquisition distance.
The missile range was 40 km when fired from 200 meters above sea level, 70 km fom 5,000 meters and 100 km from 10,000 meters. The missile also was compatible with other
aircraft types that are beyond the scope of this Web site.
The "Kilter" ARM was diversly appreciated by Western intelligence services that feared that it could have been used as an anti-AWACS weapon!
(3)
Kh-58 missiles also could be armed with a TK-57-08 nuclear warhead. Were such weapons stored at Werneuchen?
(4)
According to Anatoliy Karavan, a former 931.OGRAP pilot who also took part in the MiG-25BM elimination, no aircraft of this type were ever delivered abroad.
Contrary to the assertions of some Western publications and until proven otherwise, MiG-25BM were never delivered to Iraq.
 |
931.OGRAP < Part 1 | < Part 2 |
 |
Plan du site - Sitemap |  |
