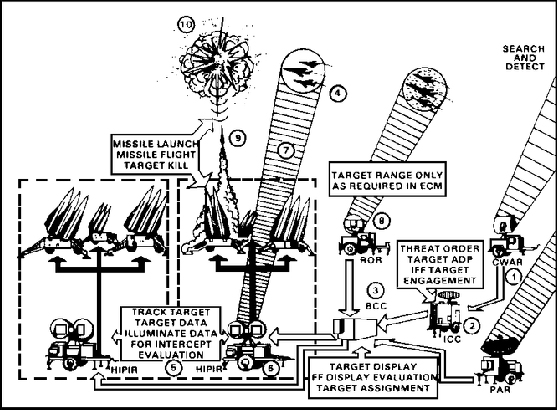

Séquence d'engagement :
Les objectifs sont détectés par deux types de radars (1). Le radar d'acquisition à ondes continues (CWAR) fournit
une couverture à basse et moyenne altitude. Le radar d'acquisition à impulsions (PAR) assure la couverture à moyenne et
haute altitude à grande distance. Après détection d'une cible, la centrale de coordination de l'information (ICC) (2)
coordonne l'identification IFF et le traitement des données automatique (ADP) relatives aux informations de la cible.
La centrale de contrôle de la batterie (BCC) (3) affiche les informations sur la cible, reçues par liaison datalink
(ATDL) - pas opérationnel dans les bataillons belges - ainsi que les informations reçues des radars et de l'ICC.
L'officier de contrôme tactique (dans le BCC) selectionne les objectifs (4) à engager et leur assigne une section
de tir (5). Le radar illuminateur haute puissance (HIPIR) (6) suit les objectifs (7) et envoie un signal de référence
au missile. Dans un environnement de contre-mesures électroniques, le ROR (8) fournis les informations de distance pour
l'engagement de la cible. Après lancement, le missile (9) se dirige sur l'objectif en comparant continuellement le signal
transmis par le HIPIR avec le signal réfléchi par l'objectif. Le missile Hawk suit un cap proportionnel en
utilisant ces informations pour corriger constamment sa course jusqu'à la cible. © GlobalSecurity.org.
System Operation (Engagement Sequence):
The Hawk system detects targets with two types of acquisition radar (1). The continuous-wave acquisition radar
(CWAR) provides low-to-medium-altitude detection coverage. The pulse acquisition radar (PAR) provides medium-to-high-altitude,
medium-range detection coverage. Following detection, the information coordination central (ICC) (2) allows for target IFF, and
automatic data processing (ADP) of target information. The battery control central (BCC)(3) displays target information received
over the Army tactical data link (ATDL) from the AN/TSQ-73, as well as information received from the radars and the ICC.
The tactical control officer (in the BCC) selects targets (4) for engagement and assigns them to a firing section (5). The
high-power illuminator radar (HIPIR) (6) tracks the targets (7) and provides a reference signal to the missile. In an electronic
countermeasures environment, the ROR (8) furnishes ranging information for target engagement. After launch, the missile (9) homes
on the target by continuous comparison of the transmitted signal of the HIPIR with the reflected signal from the target. Using
this information to make continuous adjustments in its course, the Hawk missile flies a proportional navigation course to the kill
point (10). © GlobalSecurity.org.
